We want our support like we want our food: fast, easy, and hitting the spot. Waiting for support can be infuriating for your users. Self-serve knowledge bases are swooping in to beat the bots, save time, and quell users’ hunger for further product knowledge.
A self-serve knowledge base empowers customers to find answers and resolve queries on their own terms. In fact, Zendesk has found that 69% of customers prefer this over sending tickets and waiting in queue to speak to a support rep. What’s more, it saves your customer service teams the time and effort spent on answering repetitive questions. Win-win, right?
This article will give you a tried-and-tested framework for designing your own SaaS help center with examples and tools to use because no one likes a hangry user.
A knowledge base is a centralized library of product information compiled as how-to articles, stepwise guides, FAQs, tutorials, and more
The goal of a self-serve knowledge base is to let users solve their problems independently, without relying on a support agent
A good knowledge base also reduces the mundane work for your customer-facing teams, freeing up their time for more critical customer requests
To design a fail-proof knowledge base, you need to define a solid structure, seamless navigation, and UX/UI design for your content
Remember to make your self-serve content as engaging and scannable as possible to let users skim through it and find the answers they need
What is a knowledge base?
A knowledge base (KB) is a self-serve digital library of information about your product. It educates users about every aspect of your product through video tutorials, how-to articles, step-by-step instructions, guides, Q&As, and more.
While companies also create internal knowledge bases for employees, a customer-facing knowledge base is a part of software documentation that educates new and existing users about the product’s functionality.
An external knowledge base ideally includes a search bar, feature-specific categories, and the option to contact support. Whether you call it a knowledge base, help center, resource hub, or product training center, make sure it’s comprehensive enough and well-structured.
For example, this is what Chameleon’s Help Center looks like. Our users can quickly find what they are looking for via the search or browse through the articles, tutorials, video courses, FAQs, and other resources in 14 different sections, categorized for easier navigation.
5 reasons why SaaS companies need a knowledge base
A knowledge base speeds up the time to resolution (TTR) and offers convenience to your users. But that's not all. This library of help docs and videos can also help you:
Maximize customer satisfaction: Support tickets and calls create friction in the user experience. Instead, knowledge base articles make your users self-sufficient and increase customer retention.
Deliver seamless onboarding: A solid knowledge base enables new users to fully understand the product functionality and get the best out of your tool. Self-serve support streamlines the onboarding process, nudging users to activation faster.
Empower customer success teams: A well-designed KB means your support reps don't have to answer the same old questions. They can focus on solving more complex and high-value problems.
Offer long-term customer education: By freeing up your customer service team's time, you can invest their efforts in building long-term value for your users by updating your customer education content.
Reduce operating costs: Knowledge base content can reduce the number of urgent inquiries. So, you can rely on a relatively smaller team to resolve more essential queries via tickets and calls.
Put simply, a knowledge base serves product information on a piping hot platter, delighting customers from start to finish. Let's look at the best practices to create a knowledge base for your product.
How to create a self-serve SaaS knowledge base
Creating a knowledge base from scratch can seem overwhelming. Where do you start? Which topics to cover? How do you make sure all topics align with your customer needs? There’s a lot to think about.
Don't worry; we've broken down the process of creating a self-serve knowledge base into six steps. Let’s dive in.
1. Start with keyword research and common questions
First order of business: create a list of the main keywords your customers seek help for. Look at your support tickets, help desk entries, and email requests to source the most commonly used keywords in all these queries. Word clouds are a great way of visualizing this data.
This keyword research exercise will tell you what your potential and existing customers are looking for and how they’re looking for it. Take help from your marketing department and SEO strategists to find more relevant keywords your users search for.
You can create more laser-focused knowledge-sharing content from this information. Distribute this content across your onboarding and setup process to correctly categorize your topics.
Besides this list of keywords, you can also refer to the user journey to develop potential questions or features users need help with.
With user journey mapping, you can anticipate user problems at different points of product experience. Solve these pain points and answer the most commonly asked questions for key activation points in your knowledge base.
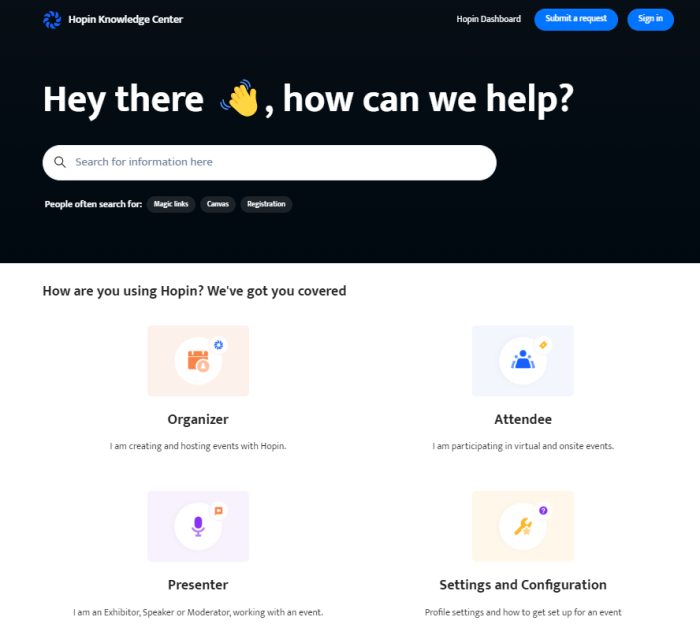
Hopin’s Knowledge Center is a great example. This portal includes a search bar with popular keywords, followed by three main types for Hopin users. You can find solutions based on which type of user you are.
Source: Hopin
2. Define the categories and structure
This is where things get exciting: you now have to chalk out the structure for your knowledge base, define the main categories, and decide what goes into which category.
Think of this exercise as planning the blog for a website—you want to have pillar pages, topic clusters, and individual blogs to cover every product function.
Use the keyword list created in step one to define the broad categories for your help center. You can also run card sorting tests to understand how users categorize information in their mental models. This can be a great research tactic to create a customer-centric design for your knowledge base that feels intuitive.
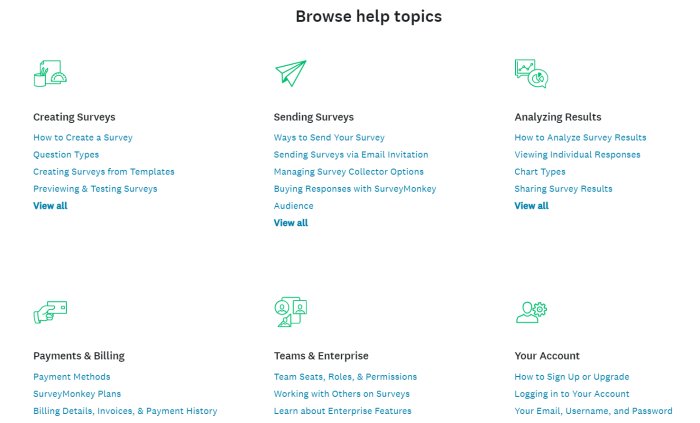
For example, SurveyMonkey’s knowledge base is divided into six main categories, each covering a crucial product function. Within each category, you’ll find more FAQs listed as individual articles.
Source: SurveyMonkey
Besides outlining the overall structure of your knowledge base, you can also create a layout for each article, helping to maintain consistency. Define different elements of each page layout, including the following.
Overall page design: Prepare a uniform layout for each page, outlining the placement for the table of contents, the question or topic, author and publishing details, options for social shares, and more.
Content formatting guidelines: Specify how the content should look once drafted. Add guidelines for including images, videos, and other media. You can also mention a tool they should use to annotate screenshots or videos for uniformity.
Related articles position: Choose a strategic position for other related articles and guides to give users more information on a topic.
Hyperlinking other resources: Set fixed guidelines for hyperlinking other articles, tutorials, courses, or videos to create a good flow of information.
This information architecture will make your help docs more uniform in design, irrespective of who's writing them. Plus, it creates an easy pattern for users to locate the correct information for any topic quickly.
3. Create reader-friendly, engaging content
Your self-serve content is only as good as how actively customers use it to resolve their doubts. Use these handy tips to maximize your knowledge base’s ease of reading by creating content your users can effortlessly understand.
Go for less text: Write brief, scannable articles in plain language to help users skim through the content and find their answers. Break big walls of text into bullet points and format the vital information in bold or italics to emphasize the details.
Add contextual links: Helps users discover new product features and boost adoption by including links to relevant resources. Point them to more in-depth articles on the topic they’re interested in.
Use visual aids: Supplement your content with instructional videos, GIFs, and screenshots for the more visual learners. This graphic material can make your product training courses more engaging and easier to understand.
Include summaries and wrap-ups: Some may not have the time to read a detailed guide word-to-word. Do your users a favor and add a TL;DR or wrap-up section in your technical support content to give them the information quicker.
Groove presents a great example of a knowledge base article, complete with skimmable text, visual content, neat formatting, and a wrap-up section.

Source: Groove
4. Create an on-brand design and format for each page
Your knowledge base should reflect your brand personality for it to tie in with all the other content you produce. Use a consistent brand voice, follow your color palette and typeface, and include branded illustrations to create a seamless user experience.
Creating a style guide is an excellent way to maintain a brand-aligned knowledge base. Lay down clear guidelines for writing and publishing knowledge base content to maintain consistency in all your articles.
To prepare a fail-proof style guide, you can cover aspects like structuring, formatting, screenshot annotations, language, and similar details.
Case in point: Codility’s knowledge base. It uses brand colors and fonts, maintaining a uniform theme throughout the help center.
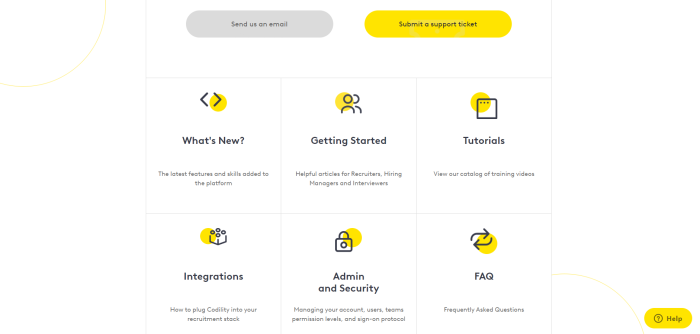
Source: Codility
5. Optimize your knowledge base for different devices
Now that it's finally time to roll out your knowledge base, test it for compatibility with various devices and screen sizes. This is particularly important since 90% of internet users worldwide use a mobile to access any website. Check how your help center website looks on mobile with Google’s mobile testing tool to create a more responsive design.
Remember to add finishing touches to your design by highlighting your CTA buttons, testing the effectiveness of your content, and streamlining the navigation for the end-users.
6. Regularly audit your knowledge base content
Building a knowledge base isn't a one-and-done process. You have to constantly audit its performance to identify gaps in the current content and rework poorly performing articles.
Here’s how you can audit your knowledge base:
Analyze customer searches to see what they’re looking for
Discover commonly asked questions that you haven’t answered
Collect customer feedback with contextual Microsurveys
Benchmark your content against each other
A good knowledge base requires regular housekeeping to resolve user queries effectively.
How to organize a knowledge base: 4 best practices
Use these tried-and-tested best practices to make knowledge management a breeze for both users and customer service teams.
1. Design easy navigation
User queries will most likely merge into multiple categories and product functions. You don't want your users to get lost in the complicated structure of your knowledge base. You might need to redefine the structure a few times, or even build out different structures, to give users an ease of use that’s unique to them.
More importantly, the information architecture (IA) can differ for different personas. Information architecture is essentially how the information is organized in a hierarchy that makes sense to every user segment. Creating a custom IA for each user persona simplifies their search for relevant answers.
For example, if you're new to Asana and jump to Asana’s help center, you'll find these neatly divided sub-sections to take you from complete unawareness to a place of total control over the tool. This knowledge base has a simple navigation designed according to the user journey once they sign up for the tool.
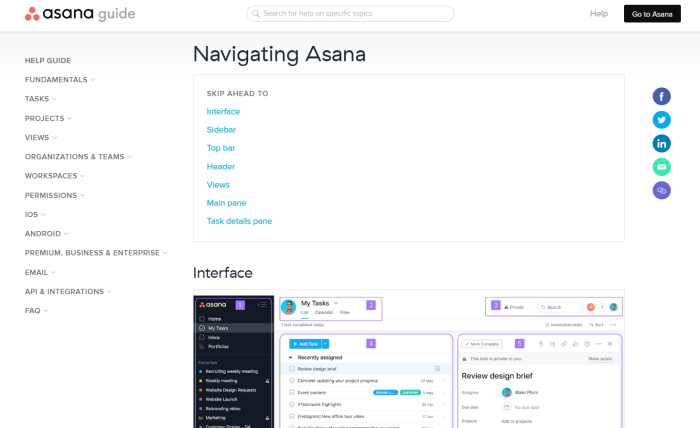
Source: Asana
2. Keep it straightforward
The success of your self-serve support depends on how quickly and conveniently it can help users solve problems. So, making your self-serve content simple and reader-friendly is a no-brainer.
Follow these golden rules to make your content more useful:
Break down long guides into smaller articles
Address a specific question in a single article or video
Use plain, jargon-free language and explain complicated terms
Go for consistent designs to deliver a smoother user experience
Remember: Your goal is to make life easy for your users. So, draft and edit your articles for readability and simplicity.
3. Make it searchable
Your knowledge base derives most of its power from how searchable it is. The more sophisticated your search performance, the higher ROI your knowledge base can produce.
Optimize your articles for search using relevant keywords that your users might search for. Spend some extra time understanding the search engine of your knowledge base software and reviewing users' search behavior to make a strong game plan for optimizing your self-serve content.
You can easily make your educational content accessible with our HelpBar, currently in beta. It works like an in-app “spotlight search” to enable your users to instantly find the answers they need – from your knowledge base, blog posts, help tutorials, live customer support, and other resources.
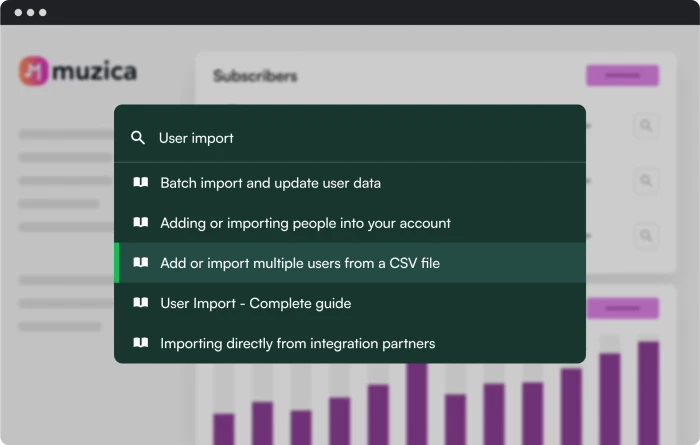
Chameleon's HelpBar in action
4. Keep it updated
Think of your knowledge base as a living and evolving portal. Keep it up to date with all the latest insights from product development, like new features, interface changes, feature enhancements, or redesigns.
Keep an eye on your customer support tickets to add and iterate your articles. Some support requests show what's missing from your help center. Use these requests to update your content consistently.
It’s always a good idea to tell users the last time your help docs were updated. This can assure that the content they’re reading is up-to-date, especially if you’re regularly releasing new features or product renditions.
We talked to Christy Hollingshead, VP of Customer Education and Engagement at Heap, and we share her insights, tips, and tricks to help you manage, scale, and improve your educational content. Dive in for expert tips.
Top 3 knowledge base tools for your SaaS help center
One of the most important factors to consider when building a knowledge base is the right knowledge base software to host your content. With so many tools, picking the right one for your needs can be tricky.
Here are three of the most popular knowledge base tools you can consider.
Tool #1: Intercom
Intercom is a customer relationship platform with a suite of tools for delivering high-quality support, like chatbots, help centers, product tours, and messenger. Companies use Intercom to streamline their communication pipeline with the end-users through multiple touchpoints.
Why choose Intercom
Here’s why Intercom can be a great knowledge base software for you:
A powerful conversation management tool to analyze and leverage customer requests
Create a library of FAQs and deliver tailored solutions to users with its in-built automation capabilities
Integrate the help center with your CRM and ticketing tools easily
Tool #2: Zendesk
Zendesk offers versatile knowledge management software for your customer-facing needs. It supports over 40 languages to solve customer queries in their language. More importantly, it has a powerful AI-powered search engine to show the most relevant results for any keyword.
Why choose Zendesk
Here’s why Zendesk can be a great knowledge base software for you:
Get in-depth insights and built-in reports to track your content performance
Moderate permission control between different teams and stakeholders
Monitor the metadata to stay on top of the latest changes in your content
Tool #3: HubSpot
HubSpot makes it easy for teams to create self-service avenues for customer support. Their knowledge base tool integrates various valuable tools like ticket management, feedback collection, automation, live chat, and more.
Why choose HubSpot
Here’s why HubSpot can be a great knowledge base software for you:
A robust reporting dashboard to measure performance and impact
Automatic sync with HubSpot’s free CRM to stay on top of all communication
Create customized KB articles with a responsive design for different screens
Consolidate all resources in your knowledge base
Exploring a new product is a gamble—like ordering a dish you’ve never tried (or even heard of) before. Things get a lot easier when someone’s on hand to talk you through things. That’s exactly what a knowledge base can do for your users, scrapping the physical limitations of someone for the 24/7 availability of tech.
A good knowledge base explains each product functionality, answers questions before a user has them, and establishes expectations.
However, designing a stellar knowledge base to fulfill these goals is where things get tricky. If you follow a half-baked strategy to only put together a FAQ section and call it a day, the results could disappoint everyone at the table.
Bookmark this start-to-finish guide on designing a knowledge base and start unlocking a seamless experience for your users today.
Integrate your knowledge base with your product
Add another layer to your user experience by linking to your help docs from product tours, onboarding checklists, and in-app help menus. Build and customize them quickly with Chameleon.